Related FAQs
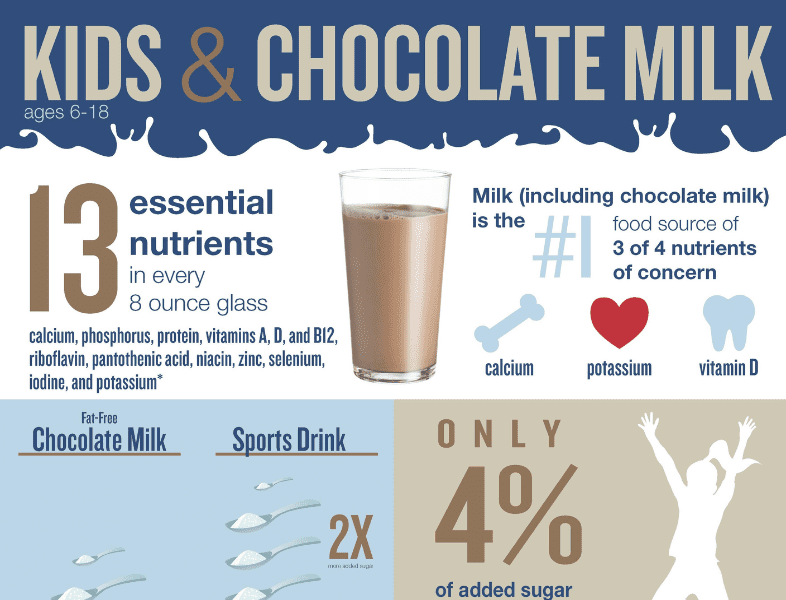
Milk is required as a part of the National School Lunch and Breakfast programs because it provides a powerful package of 13 essential nutrients that are good for overall wellness. Schools can choose to offer white and flavored, fat-free and 1% milk, as well as lactose-free milk. Low-fat and fat-free yogurt and cheese can also be part of school meals.
The Healthy Hungry-Free Kid Act, require school meal programs to meet specific nutrition standards. The standards are developed using the latest nutrition science. The school lunch and breakfast programs require milk be offered as part of the meal. While students are generally not required to take it, meals that include milk provide more nutrients than those without.
Consider the following impacts to health and nutrition if milk (flavored or not) is removed from the diet:
- Milk contains calcium, vitamin D and potassium which are nutrients of concern that most American’s don’t get enough of.
- On average, by the time children are 6 years old, milk consumption falls below the Dietary Guidelines for Americans recommended daily servings of dairy.
- Children in the U.S., who drink flavored milk, do not have higher Body Mass Indices (BMIs) compared to non-drinkers suggesting that flavored milk does not lead to weight gain.
- Replacing nutrient contribution from milk requires three to four food items but adds back more calories and fat than were originally contributed by milk
- Additional impacts
We recognize that getting students to take and drink milk can be a challenge. The following ideas might help depending on the reason for milk being left off (or on) the tray.
- Make sure the milk you are serving is very cold.
- Serve a variety of flavors.
- Consider offering Hot Chocolate Milk and/or Smoothies
- Check out our 10 ways to encourage students to drink milk
Milk taste continues to be a reason students decline to select milk with school meals. Improper storage and service temperature is one factor that can affect milk taste. Watch our Chill Out with Cold Milk webinar recording for tips on how to keep your milk as cold as possible and one free CEU and order our Free Chill Out with Cold Milk Toolkit.
You may need to contact your processor if you experience quality issues that can’t be explained by your handling and storage practices.
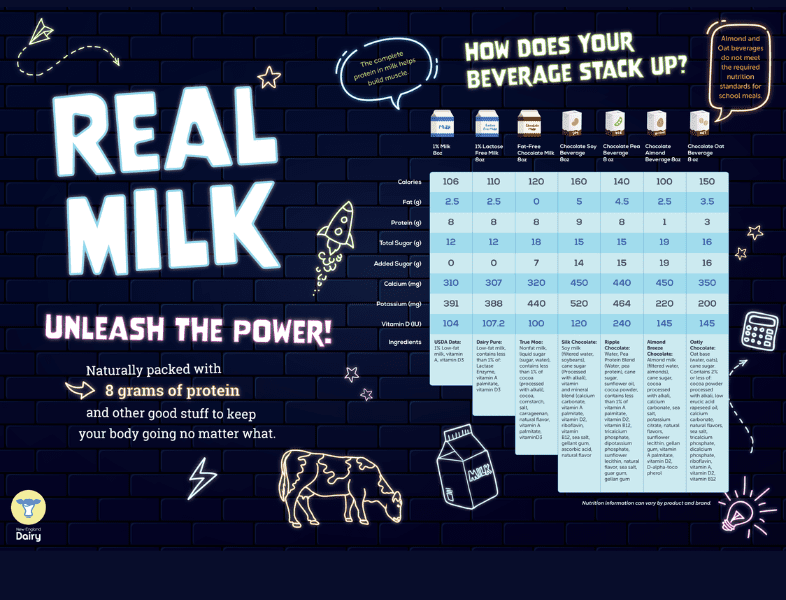
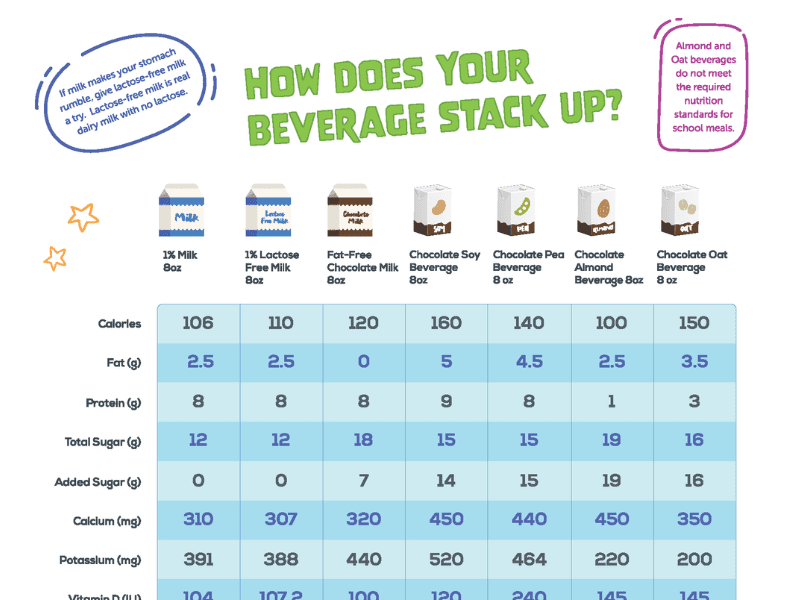
Real milk packs in a lot of nutrition, especially protein – it contains 8 grams of protein per 8 oz serving. Allowable milk alternates must first provide at least 8 grams of protein per 8 oz serving and they must contain the following minimum levels of nutrients to ensure they are providing similar nutrition to dairy milk.
| Alternative Beverage Requirements | 1% Low-fat Milk |
| Protein 8 g | Protein 8 g |
| Calcium 276 mg | Calcium 310 mg |
| Vitamin D 100 IU | Vitamin D 104 IU |
| Vitamin A 500 IU | Vitamin A 500 IU |
| Potassium 349 mg | Potassium 391 mg |
| Phosphorus 220 mg | Phosphorus 253 mg |
| Magnesium 24 mg | Magnesium 29.5 mg |
| Riboflavin .44 mg | Riboflavin .344 mg |
| Vitamin B12 1.1 mcg (micrograms) | Vitamin V12 1.5 mcg (micrograms) |
*Alternate beverage reference on page 2
Water is important for hydration and should be encouraged throughout the day. When water is consumed at meals instead of milk students often miss out on key nutrients they need more of in their diets like calcium, vitamin D, and potassium. The nutrients lost when students choose another beverage are difficult to make up with other foods while keeping to the same amount of calories and fat.