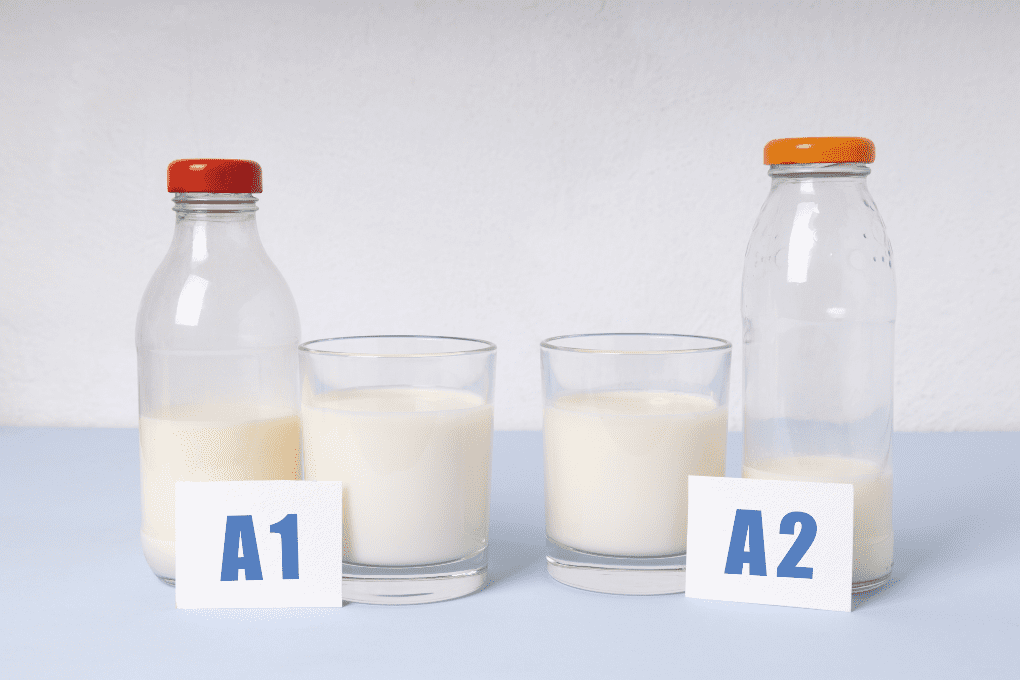
Maybe you’ve noticed a carton of A2 milk next to your go-to choice at the grocery store. Or maybe you read something about A2 milk online. But what is A2 milk and what makes it different from regular milk?
Read on to learn the answers to the top five questions we get about A2 milk:
- What is A2 Milk?
- What’s the difference between A1 and A2 milk?
- Is A2 milk lactose-free and safe for people with lactose intolerance?
- What cows produce A2 milk?
- What does the research say about A2 milk for human consumption?
So, What is A2 Milk?
A2 is a type of milk that only contains the A2 beta-casein protein, one of the main kinds of protein present in milk. A1, the type of milk most commonly found in grocery stores, contains both the A2 protein and the A1 protein. A2 milk is still cow’s milk and the nutrient levels – like calcium, potassium, and vitamin D – are the same.
When compared to drinking regular cow’s milk, some people with undiagnosed dairy intolerance have reported that drinking A2 milk does not result in discomfort. These claims are person-specific.
What’s the Difference Between A1 and A2 Milk?
The only difference between A1 and A2 milk is that A2 milk only contains the A2 protein. As previously mentioned, A1 and A2 milk proteins are two common variants of beta-casein found in cow’s milk. Cow’s milk contains 8 grams of protein per 8-ounce cup of milk, and approximately 30 percent of this protein is beta-casein.
But there’s only one difference between A1 and A2 proteins, and it’s at the 67th amino acid in the protein’s 209 chain: A1 beta-casein has a histidine and A2 a proline. When the A1 beta-casein is digested it can create the peptide BCM-7. BCM-7 is thought to cause the discomfort that results from consuming dairy products by a select group of people. However, this has yet to be definitively confirmed by the scientific community.
A2 Milk Nutrition Facts
A2 milk nutrition doesn’t vary from A1 milk nutrition of the same type, such as whole or fat-free. Milk is full of nutrients that fuel your body and keep you healthy. Check out this resource for an overview of the nutrients found both in A1 and A2 milk.
A2 Milk for Lactose Intolerance
Depending on how severe an individual’s case of lactose intolerance is, they may be able to consume A2 milk. Currently, research is varied when it comes to whether or not you can drink A2 milk for lactose intolerance, but some individuals have self-reported lesser or a lack of symptoms after consuming it.
So, is A2 milk lactose-free since some people with lactose intolerance can drink it? No, A2 milk still contains lactose, which is why anyone diagnosed with lactose intolerance should be cautious when trying it.
It’s important to note that many people who experience discomfort after consuming dairy products may not actually have lactose intolerance. They could instead have a milk protein allergy, which is an immune response to the casein or whey proteins found in milk, or a dairy intolerance. Only a doctor can diagnose the reason behind discomfort after consuming milk or dairy.
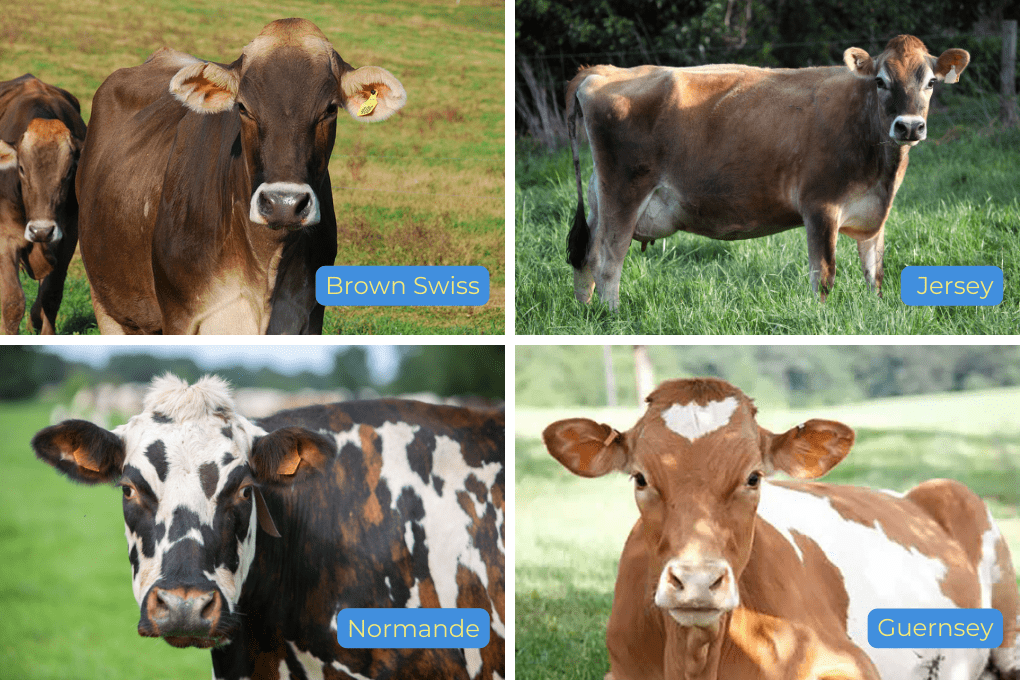
What Cows Produce A2 Milk?
There’s no specific breed of cow that produces A2 milk. The A2A2 gene causes cows to produce only the A2 protein, instead of both proteins. Brown Swiss, Jersey, Normande, and Guernsey have the highest levels of this gene. Milk can be tested for the beta-casein that it contains, which is how A2 cows are found.

What Does the Research Say: Benefits of A2 Milk
Claims that A2 milk reduces dairy-related inflammation, heart disease risk, or type 1 diabetes risk have not been supported by scientific studies. The health benefits of A2 milk remain a theory, and more research is needed.
Regardless of what carton you choose, know that cow’s milk is a healthful and wholesome choice. Research has linked cow’s milk consumption to improved blood pressure, reduced risk of type 2 diabetes, and reduced risk of cardiovascular disease.
Should You Drink A2 Milk?
While the science is currently inconclusive on its added health benefits, A2 milk contains the same 13 essential nutrients as regular milk, so it is a healthy choice to nourish your body. For most people, it doesn’t matter whether they choose A1 or A2 milk, but for those that self-report reduced discomfort when drinking A2 milk, it can be a great option. Whether you choose A1 or A2 milk, choosing cow’s milk is a healthy and sustainable option for your diet.